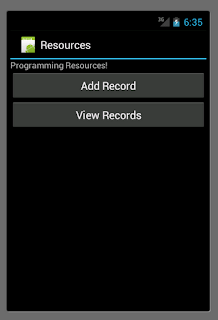
I wanted to redo the database in the simplest way possible to make things clearer. To do this I made a simple initial form with two buttons:
I still needed to create the sqlHelper class. But this time I only created a single table. Here is the code for the SqlHelperClass
package com.spconger.programmingresourcesdata;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class SqlHelperClass extends SQLiteOpenHelper{
/*
* This class extends SqlLiteOpenHelper
* It creates the database and the tables
* and sets static constants that are used
* in the other classes
*/
//set database as priiate constatn
private static final String DATABASE_NAME = "ProgramResources.db";
private static final int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
//public constants
//database table
public static final String TABLE_NAME="Book";
//columns
public static final String BOOK_ID="bookId";
public static final String BOOK_TITLE="title";
public static final String BOOK_AUTHOR="author";
public static final String BOOK_RATING="Rating";
//required constructor
//takes the contest which is usually the current
//activity, it also passes the database name and
//version to the super class
public SqlHelperClass(Context context) {
super(context, DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
// here we create the table
String sql_Book="CREATE TABLE " + TABLE_NAME
+"(" + BOOK_ID + " integer primary key autoincrement, "
+ BOOK_TITLE + " text not null, "
+ BOOK_AUTHOR + " text not null, "
+ BOOK_RATING + " int, "
+ "unique (" +BOOK_TITLE + "))";
//add the table to the database
db.execSQL(sql_Book);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
//You should put code here to handle new versions of the database
}
}
Here is the form for adding records
The java behind this form is fairly straight forward. I just initialize a writable database, get the values from the EditText controls and insert them into the database
package com.spconger.programmingresourcesdata;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class AddRecordsActivity extends Activity{
/*
* This activity adds records to the database.
* I purposefully kept this simple
* not breaking it into too many methods
* Consequently the AddRecord method does
* more than it probably should
*/
EditText txtTitle;
EditText txtAuthor;
EditText txtRating;
Button btnSave;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.addrecords);
btnSave = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button1);
btnSave.setOnClickListener(new AddRecordListener());
}
private class AddRecordListener implements View.OnClickListener{
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//get database
SqlHelperClass sqlHelper = new SqlHelperClass(AddRecordsActivity.this);
SQLiteDatabase db= sqlHelper.getWritableDatabase();
//get the values from the EditText controls
txtTitle = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editTextTitle);
String title=txtTitle.getText().toString();
txtAuthor=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.editTextAuthor);
String author=txtAuthor.getText().toString();
txtRating = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editTextRating);
String ratingString=txtRating.getText().toString();
int rating=Integer.parseInt(ratingString);
//add the values from the EditViews to the columns
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(SqlHelperClass.BOOK_TITLE,title);
values.put(SqlHelperClass.BOOK_AUTHOR, author);
values.put(SqlHelperClass.BOOK_RATING, rating);
//Insert into the database
long book_id= db.insert(SqlHelperClass.TABLE_NAME, null, values);
db.close();
//if the insert is successful
if(book_id != -1)
{
//start a toast (a message)
Toast toast = Toast.makeText
(AddRecordsActivity.this, "Record Added", Toast.LENGTH_LONG);
toast.show();
}
else
{
Toast toast = Toast.makeText
(AddRecordsActivity.this, "Record failed to Insert", Toast.LENGTH_LONG);
toast.show();
}
//clear for next record
clearForm();
}
}
private void clearForm()
{
txtTitle.setText("");
txtAuthor.setText("");
txtRating.setText("");
}
}
finally we just view the records. I didn't do anything fancy. I created a cursor to look through the records and appended them to a string that terminates with a new line character. Then I set the resulting text to the ViewText. Here is the codeL
package com.spconger.programmingresourcesdata;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ViewRecordsActivity extends Activity{
/*
* Again, to make this simple, the getRecords method
* does more than one record should do
*
*/
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.viewrecords);
getRecords();
}
private void getRecords(){
//initiate the SqlHeperClass and get the database
SqlHelperClass sqlHelper = new SqlHelperClass(ViewRecordsActivity.this);
SQLiteDatabase db= sqlHelper.getWritableDatabase();
//create an array of the columns
String[] columns = new String[]
{sqlHelper.BOOK_TITLE,
sqlHelper.BOOK_AUTHOR,
sqlHelper.BOOK_RATING};
//start a cursor to move through the records
Cursor cursor = db.query(sqlHelper.TABLE_NAME, columns, null, null, null, null, null);
String result="";
//use the cursor to loop through the records
for(cursor.moveToFirst();!cursor.isAfterLast();cursor.moveToNext()){
//I am just concatenating the records into a string
//terminated by a line break
result+= cursor.getString(0) + ", " + cursor.getString(1) + "--" + cursor.getInt(2) + "\n" ;
}
//assign the result to the textview
TextView content=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.content_list);
content.setText(result);
}
}
Here is the the activity running


No comments:
Post a Comment